L-Dex Analysis
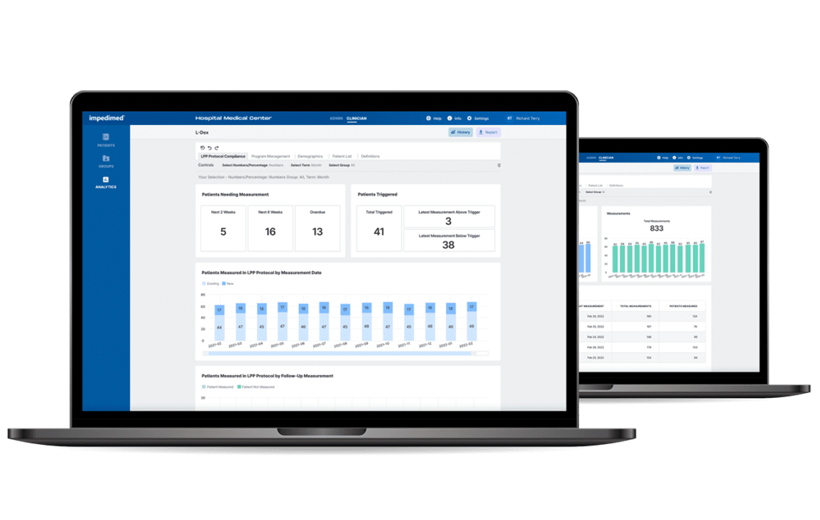
L-Dex Analytics
Optimize Patient Outcomes With Reporting and Insights Generated Directly From Your SOZO Data.
- Optimize workflows and patient outcomes
- Track utilization of L-Dex on your SOZO devices
- Understand your L-Dex patient population
Designed for Lymphedema
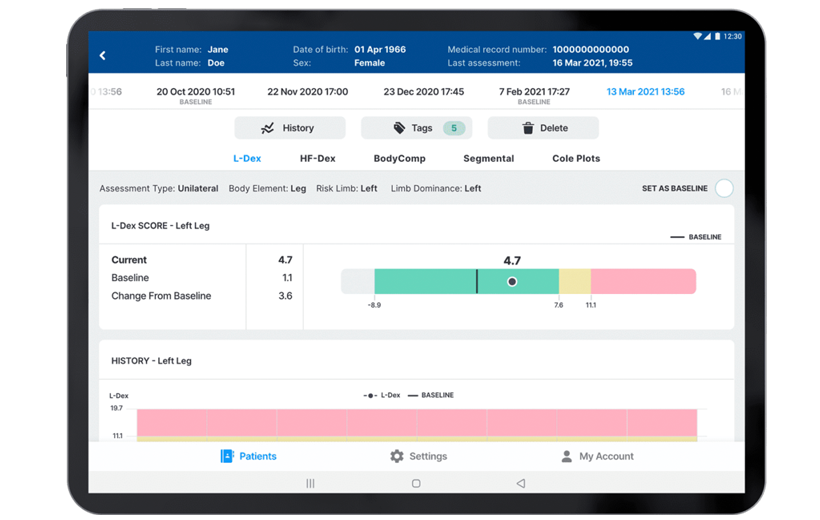
- The L‑Dex score, only available from ImpediMed, is designed to detect small lymphedema-related fluid changes in the limbs.
- L‑Dex compares the fluid in a limb at-risk for lymphedema to a healthy limb in order to help detect lymphedema.
- FDA-cleared for unilateral and bilateral secondary lymphedema of the arms and legs, in women and men.
Accurate Detection
- L‑Dex is validated to detect lymphedema at its earliest, subclinical stage
- Detects fluid changes as small as 36 ml (2.4 tablespoons)¹
Validated against lymphoscintigraphy² - 80% Sensitive and 90% Specific in detecting subclinical lymphedema following cancer surgery with a 6.5 change from a pre-treatment baseline³
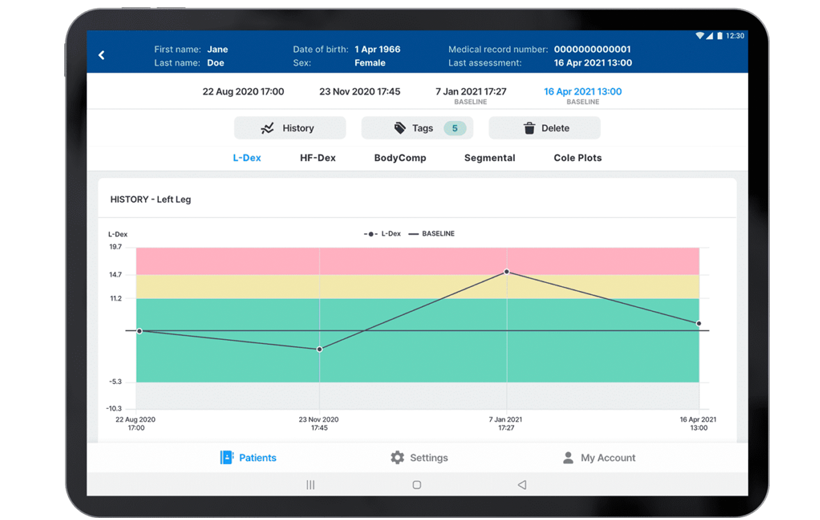
Demonstrated Outcomes
- 92% of patients with early detection using L-Dex and intervention did not progress to chronic lymphedema4
- Significantly lower progression to chronic lymphedema with early detection using L-Dex and intervention versus using tape measure4
- L-Dex more precise and reliable than tape measure4
Extensive Experience
- 16 of the 31 members of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®) use SOZO with L-Dex
- BIS is recommended in lymphedema clinical practice guidelines from the American Physical Therapy Association5, eviCore Healthcare6, and the National Lymphedema Network7
- Major institutions including University of Kansas, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Memorial Sloan Kettering, and MD Anderson have published their experience using L-Dex8-11
References
- Ward, L. Is BIS ready for prime time as the gold standard measure. Jrn Lymphoedema 2009;4(2).
- Dylke ES, et al. Diagnosis of upper limb lymphedema: development of an evidence-based approach. Acta Oncologica 2016;55(12):1477-83.
- Fu MR, et al. L-Dex ratio in detecting breast cancer-related lymphedema: reliability, sensitivity, and specificity. Lymphology 2013;46:85-96.
- Ridner SH, et al. A Comparison of Bioimpedance Spectroscopy or Tape Measure Triggered Compression Intervention in Chronic Breast Cancer Lymphedema Prevention. Lymphatic Research and Biology 2022.
- Shah C, et al. The impact of monitoring techniques on progression to chronic breast cancer‑related lymphedema: a meta‑analysis comparing bioimpedance spectroscopy versus circumferential measurements. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment 2020; https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-020-05988-6.
- Levenhagen K, et al. Diagnosis of Upper Quadrant Lymphedema Secondary to Cancer: Clinical Practice Guideline From the Oncology Section of the American Physical Therapy Association. Physical Therapy 2017;97(7):729-45.
- Clinical guidelines for medical necessity review of physical and occupational therapy services. Version 1.0.2019. eviCore Healthcare.
- Position statement of the National Lymphedema Network: the diagnosis and treatment of lymphedema. NLN Medical Advisory Committee; February 2011.
- Kilgore L, at al. Reducing breast cancer-related lymphedema (BCRL) through prospective surveillance monitoring using bioimpedance spectroscopy (BIS) and patient direction self-interventions. Ann Surg Oncol 2018;http://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-018-6601-8.
- Soran A, et al. The importance of detection of subclinical lymphedema for the prevention of breast cancer-related clinical lymphedema after axillary lymph node dissection; a prospective observational study. Lymph Res Bio 2014;12(4):289-94.
- Wiser I, et al. Preoperative assessment of upper extremity secondary lymphedema. Cancers 2020;12(135):doi:10.3390/cancers12010135.
- Coroneos CJ, et al. Correlation of L-Dex Bioimpedance Spectroscopy with Limb Volume and Lymphatic Function in Lymphedema. Lymph Res & Bio 2018;doi:10.1089/lrb.2018.0028.